General Information
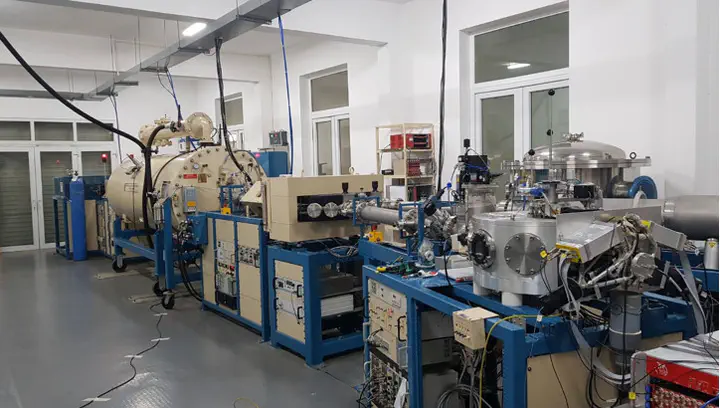 HUS Pelletron Accelerator Facility
HUS Pelletron Accelerator FacilityHUS Pelletron Accelerator is the leading research accelerator facility in Vietnam. It is one of the highlight facilities of the “Laboratory for Ion beam and Nuclear Applications” (LINA), Department of Nuclear Physics, Faculty of Physics.
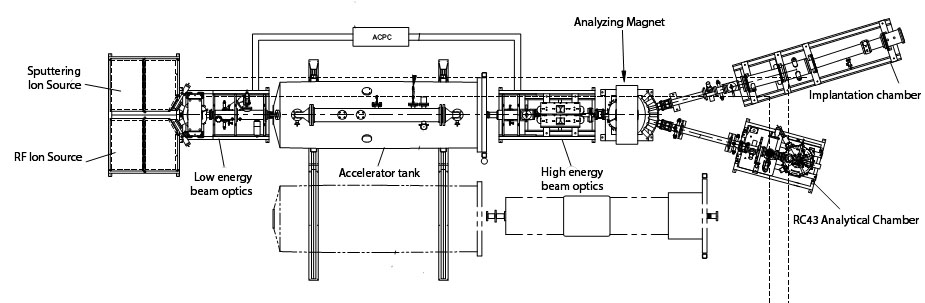
The Pelletron Accelerator was installed and commissioned in 2011 and experiments using the beam were started in 2012. Charge particles are produced by either two ion sources located at the front section of the accelerator hall: The NEC RF Charge Exchange Ion Source (Alphatross) and Negative Ions by Cesium Sputtering (SNICS) Ion Source. The RF ion source is capatable of producing negative ions of Hydrogen and Helium as the original form of gas. The Cesium Sputtering ion source generates sputtered negative ions by accelerating the ionized Cesium stream toward negative charged cathode made by the ion species intented to be produced. The negative ions are pre-accelerated to low energies (20-30 keV) using bias voltages in a short section. They are then bent through 45o using an injector magnet into the low energy side (first stage) of the accelerating column. In the first stage, the acceleration results from the electrostatic attraction of the negative ions by the positively charged high voltage terminal situated at the center of the column. The high electric potential at the terminal is achieved by a continuous transfer of charge to the terminal by means of the chain of steel pellets and hence the name Pelletron accelerator. Inside the terminal the ions pass through a small volume of continuously-circulated Nitrogen gas, where they lose electrons and become positively charged. The average charge of the ion depends upon the type of ion and the terminal voltage. The resulting positive ions now enter the second or high energy stage of acceleration where the positive voltage of the terminal acts repulsively on the positive ions. In this way, the final energy of the ion that has acquired a positive charge of n units will be (n +1)V, where V is the terminal voltage (maximum of 1.7 MV). For example, the final energy at the maximum terminal voltage for 12C3+ is 6.7 MeV. Beams ranging from protons to Uranium can be accelerated.
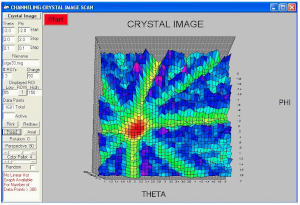
The accelerated ion beam can be delivered into two application beamlines: The IBA beamline and the MeV-ion implantation beamline. The IBA beamline is equiped with the NEC RC43 analytical endstation, which is designed for analytical applications using Ion Beam Analysis techniques, namely the Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry (RBS) and Channeling analysis, Elastic Recoil Detection Analysis (ERDA), Nuclear Reaction Analysis (NRA) and Particle-induced X-rays Emission (PIXE). The Ion implantation beamline is equiped with a Raster Scanner, a beam profile monitor and precise current monitor system. The Raster Scanner system uses a fast changing electrostatic field to sweep the MeV ion beam (delivered by the accelerator) along X-Y axes and produce various implantation pattern over a large area (typically 10 cm x 10 cm) of the implantation target.
Maintaining good vacuum in the entire beam line is required. Pump stations comprising of rotary pump and turbo molecular pump are installed along the beam path to maintaince ultra high vacuum down to 10-8 - 10-7 Torr.
The Pelletron Accelerator produces radiation when the ion beam is extracted. In the case of HUS pelletron, the beam energy and intensity are sufficiently low that the level of ionizing ratiation leaked outside of vacuum enclosures is always well bellow the exemption level. Nevertheless to ensure radiation safety, an ambient radiation monitor with an alarm system is installed inside accelerator hall and constantly operated.
Besides the routine operation of the accelerator, major efforts of local staff members have been made towards maintenancing key parts of the accelerator system such as RF and SNICS ion sources, accelerator tank and its inner structures, and IBA beamline. In 2014, a major maintenance for the accelerator has been performed by our staffs. The accelerator tank was openned and its inner structures such as charging chain, terminal sphere, mechanical parts, blower systems… was inspected and cleanned. It is found that the charging chain was losen and some mechanical supports felt apart, which can result in a chain failure. All these potential issues has been fixed during maintenance period. The insulation SF6 gas and drying agents was also refreshed. As a result, a stable operation has been achieved with minimal leakage currents and stable current drains in both two charging chains.

The beam time for HUS Pelletron Accelerator are flexible and accessible for external users. Just send us your requests here for beam time proposals and further inquiries.